|
|

A database of Enzyme Catalytic Mechanisms
How to use the
 in the EzCatDB
in the EzCatDB
DB code:
You can input the code in the "DB code" column and click the "search" button at your right if you have a DB code for this database.
You can use the form below to specify the enzymes that you seek:
Enzyme Name in UniProtKB:
To search by a specific "protein name" or "synonyms" in the UniProtKB data, input it in this column and click the "search" button below.
Enzyme Name in KEGG:
To search by a specific "name" in KEGG enzyme data, input it in this column and click the "search" button below.
E.C.:
You can input the number in the four rows of "E.C." if you have a specific Enzyme Commission (E.C.) (four-digit) number. Here, you can abbreviate some numbers. For instance, you can search by E.C. numbers, such as "3.2.-.-" or "-.2.1.-" by leaving the third and fourth rows or the first and fourth rows empty, respectively (see Enzyme Nomenclature at IUBMB).
CATH:
You can put CATH (four-digit) numbers in the four rows to search by a specific protein domain structure. Even without such numbers, to search for enzymes that have alpha-structure domain, beta-structure domain, mixed alpha-beta structure domain, or few secondary structures, you can put 1, 2, 3, or 4, respectively, in the first row, and leave the others empty.
PDB:
A specific PDB entry code (four-digit code) can be queried.
KEGG pathway:
You can search for enzymes by code that are involved in a specific metabolic pathway. Use KEGG metabolic pathway code, eight-digit code beginning with "map".
UniProtKB; Accession number:
A specific UniProtKB accession number (six-digit code) can be queried.
Active-site residues:
You can input as many as three active-site residues, such as catalytic residues and metal-binding residues, using three-letter codes of amino acids (such as ASP and HIS).
PubMed ID:
You can search for the enzyme data that are cited in a specific paper. Use its reference ID in the PubMed bibliographic database.
Author name (reference):
You can search for enzyme data that are cited in specific papers. Use the author family name.
Key word (reference title):
You can search by the key words in the title for enzyme data that are included in specific papers.
KEGG compound ID:
You can search for enzymes that interact with a specific compound or ligand as cofactors, substrates, or products, by code. Use KEGG COMPOUND code, six-digit code beginning with "C", or EzCatDB compound code, six-digit code beginning with "L".
Ligand names:
You can search for enzymes that interact with specific ligand molecules as cofactors, substrates, or products. You can input as many as three ligand names in the right columns. Those ligand molecules can be specified, by selecting "cofactor", "substrate", or "product" from the left-hand menu.
Ligand types:
You can search for enzymes that interact with specific ligand molecules as cofactors, substrates, or products. You can select as many as three ligand types (such as "peptide", "nucleotide", or "phosphate group") from the right menu. Selecting "cofactor", "substrate", or "product" from the left menu can specify those ligand molecules.
Ligand annotation types:
Annotation types of ligand molecules (bound/analogue bound/unbound) can be queried.
Right-hand menu:
The following can be selected.
"All Unbound":
You can search for enzyme data in which all the ligands (for cofactors, substrates, products, or intermediates) have been annotated as "Unbound" for all the PDB data. To do so, select "All Unbound" from the right menu for each category ("cofactors", "substrates", "products", or "intermediates") that is selected from the left menu.
"Unbound":
Entries for which any ligand molecule has been annotated as "Unbound" for all PDB data, can be retrieved by selecting "Unbound", for each category.
"Not annotated":
Furthermore, because it is difficult to annotate some ligands such as water molecule (H2O) and H+ (proton) ion, entries with any ligand that cannot be annotated can be retrieved by selecting "Not annotated".
"All Unbound/Not annotated":
Entries with either "Unbound" or "Not annotated" for all ligands can be retrieved by selecting "All Unbound/Not annotated" from the right-hand menu.
"Bound" or "Analogue Bound":
Moreover, you can search for enzyme data in which any ligand (for cofactors, substrates, products, or intermediate) has been annotated as "Bound" or "Analogue" for any PDB data. To do so, select "Bound" or "Analogue Bound", respectively, from the right menu, for each category ("cofactors", "substrates", "products", or "intermediates") that is selected from the left menu.
"Bound or Analogue Bound":
Entries with either "Bound" or "Analogue Bound" can be retrieved by also selecting "Bound or Analogue Bound".
Left-hand menu (for cofactors, substrates, products or intermediates):
For all categories ("cofactors", "substrates", "products", or "intermediates"), "-" can be selected from the left menu. Regarding substrates and products, all entries are presumed to belong either to "All Unbound/Not annotated" category or to the "Bound or Analogue Bound" one.
Catalytic domain:
You can seek enzyme data for which catalytic domain structures have been determined and annotated. Simply check "include". You can search for data by checking "exclude" to exclude those enzyme data. "All" is selected as the default to include all data.
Active-site residues annotated:
You can seek enzyme data for which active-site residues have been annotated. Check "include". Data are searchable by checking "exclude" to exclude those enzyme data. "All" is selected as the default to include all data.
Literature for catalytic mechanisms:
You can search for enzyme data that has been cited in any publication that has reported on catalytic mechanisms. Check "include". You can search for data by checking "exclude" to exclude those enzyme data. "All" is selected as the default to include all data.
RLCP classification:
You can search for enzyme data whose catalytic mechanism has been classified in the RLCP classification by checking "include". You can search by checking "exclude" to avoid those enzyme data. "All" is selected as the default to include all data.
If no enzymes are specified, all entries in the EzCatDB will be listed.
You can combine the above information to specify enzymes in the following way:
To search for those enzymes with alpha-beta structures, E.C. 3.1.-.-, and magnesium as cofactor, you can input "3" in the first row of CATH, "3" and "1" in the first and second rows of E.C., respectively, and select a cofactor from the left menu of ligand name, and put "magnesium" in its right-hand column. You can obtain the enzyme data list by clicking the select button.
An example of search
An example is shown below.
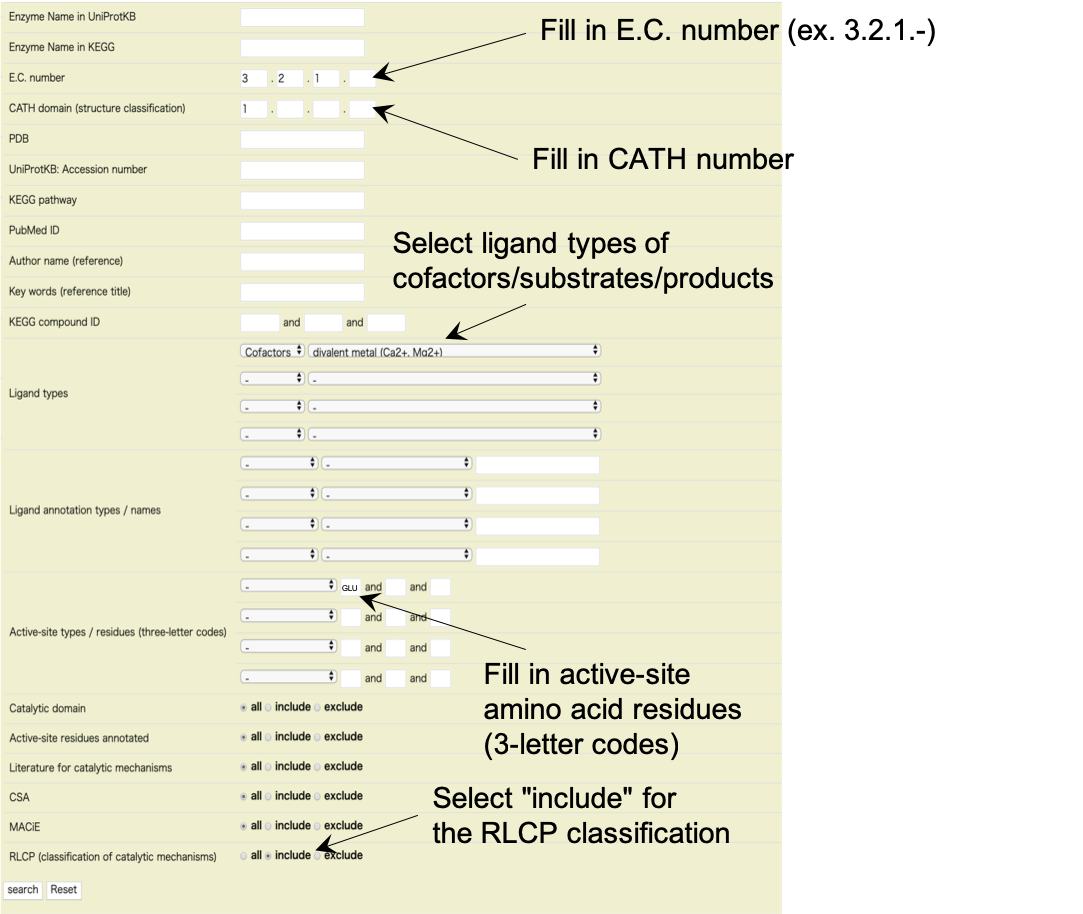
And then, click the "search" button.
4 entries are found.

|

